This project focusses on the design, building and testing of an inverter circuit (DC to AC).
The last few years have seen rapid developments in the area of power electronics, including new switching devices, new topologies and new control algorithms. With new renewable energy generation targets being set as well as emerging capabilities due to improved battery technology, inverters are key to transparent conversion between power distribution domains. Understanding how to build cheap, small, reliable and efficient inverter circuits is key to maximising the utility and performance of these devices.
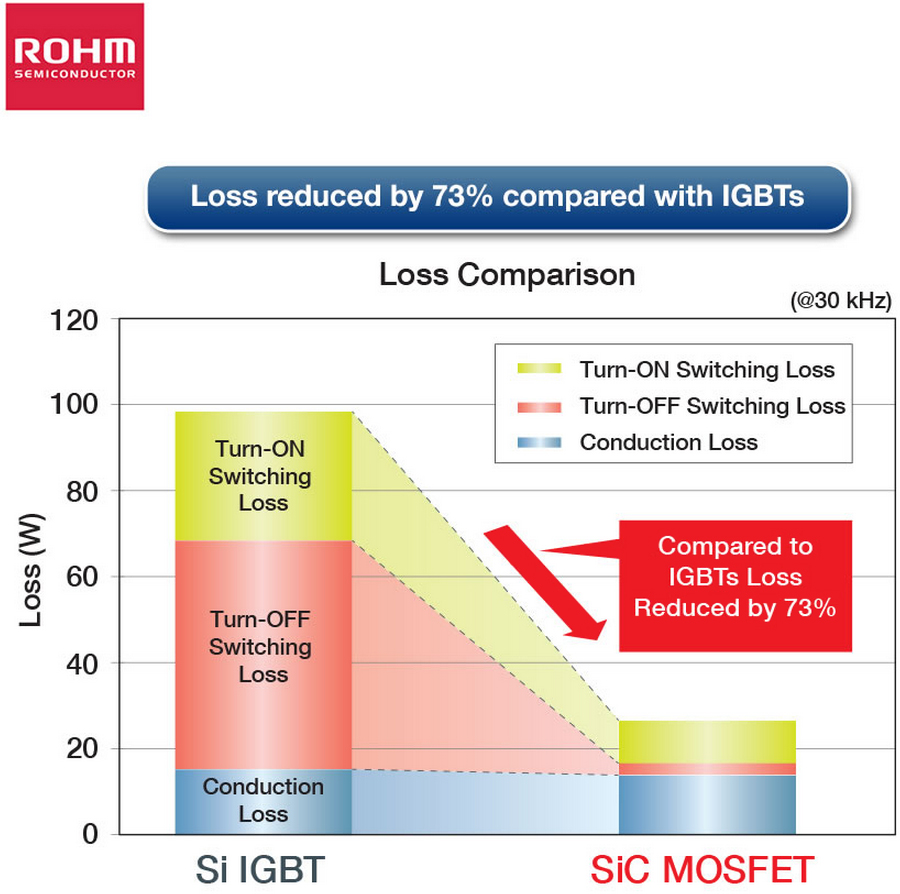
Silicon carbide (SiC) semiconductors are a fairly recent addition to the mass-produced transistor market. A SiC-based inverter circuit should be more efficient and able to operate at higher switching frequencies as compared to a traditional silicon (Si) based inverters. This should enable the overall efficiency to improve. In addition, there should be a significant size and weight reduction of the inverter. One of the main challenges with a SiC-based inverter is the high switching speed, making it potentially difficult to drive them.
A complementary project has been created to design new inverter control algorithms, and these can potentially be tested on the resulting prototype.
The exact scope, content and outcomes of the project will be agreed upon with the students considering their background and interests.
Expected outcomes
- Designing an inverter based the emerging wide-bandgap (WBG) silicon carbide semiconductor.
- Employing multiple inverters to form a multilevel inverter, providing increased dynamic performance.
- Implementing a simple modulation scheme (e.g. pulse-width modulation) using a micro-controller or FPGA (should be done using a rapid prototyping platform).
- Evaluating the performance, determining the operating limits.
- Potentially implementing control methods developed by complementary project.
Resources
- Digital and analog circuit components and ICs.
- Manufacturing of printed circuit boards.
- Micro-controller or FPGA development kit (with Embedded or HDL Coder support).