This project will look at the generation of dithering signals used to improve the response of switched conversion systems.
Physical implementations of digital-to-analogue converters (DACs) introduce various non-ideal effects, including element mismatch, thermal and semiconductor noise, slew-rate limitations, and glitches caused by non-ideal transistor switching. These effects come in addition to the fundamental error sources of aliasing and quantisation that occur in a digital signal processing system, due to discretisation in both in time and value.
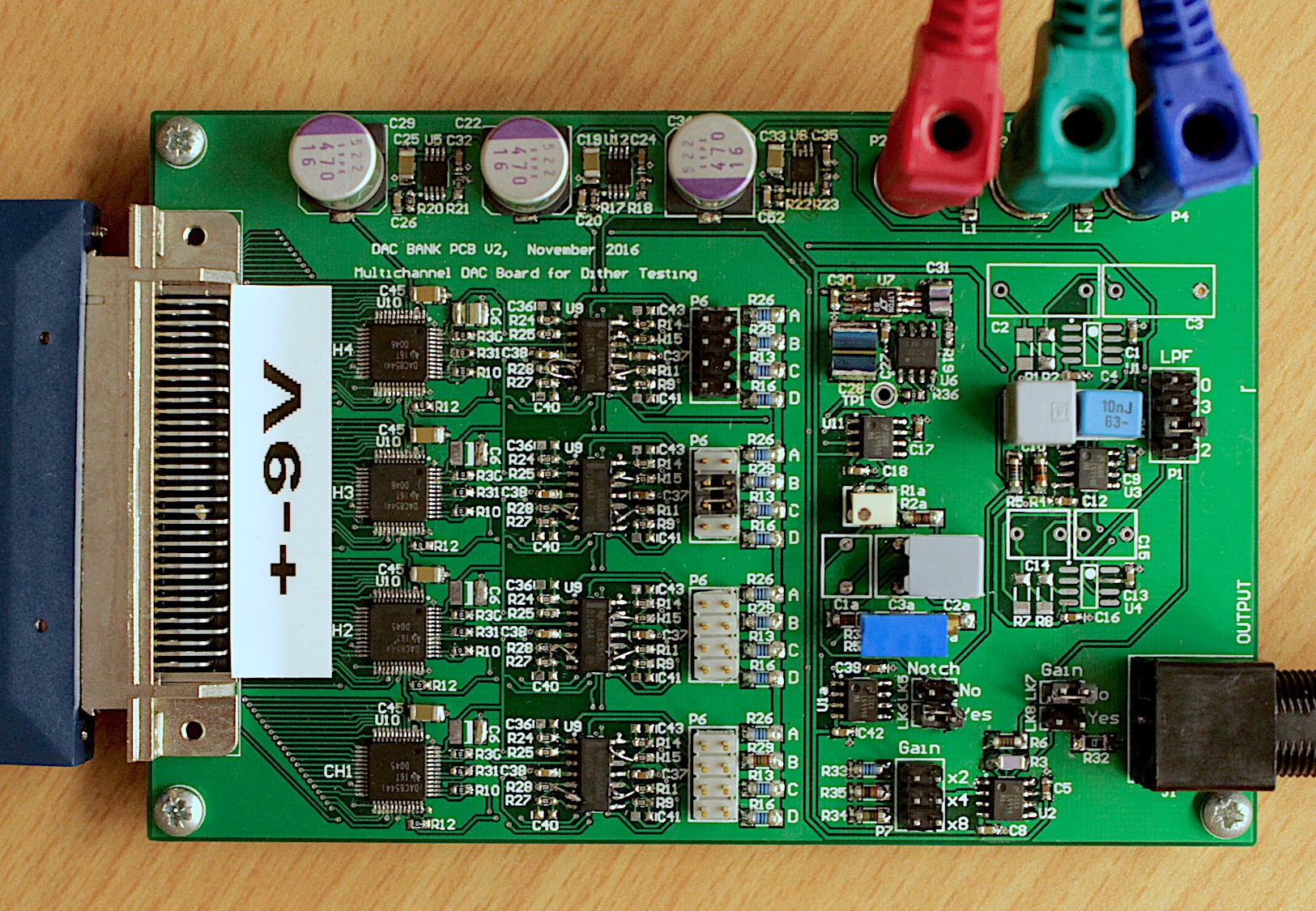
When applying a DAC for high precision motion control, DAC-errors deteriorate the achieved performance. Hence, it is of interest to mitigate them. Aliasing is reduced by reconstruction filtering and interpolation, and quantisation error is eliminated using small-scale noise dithering. Element mismatch can be compensated for using several methods, such as dynamic element matching or physical calibration, and slewing can be partially reduced by oversampling.
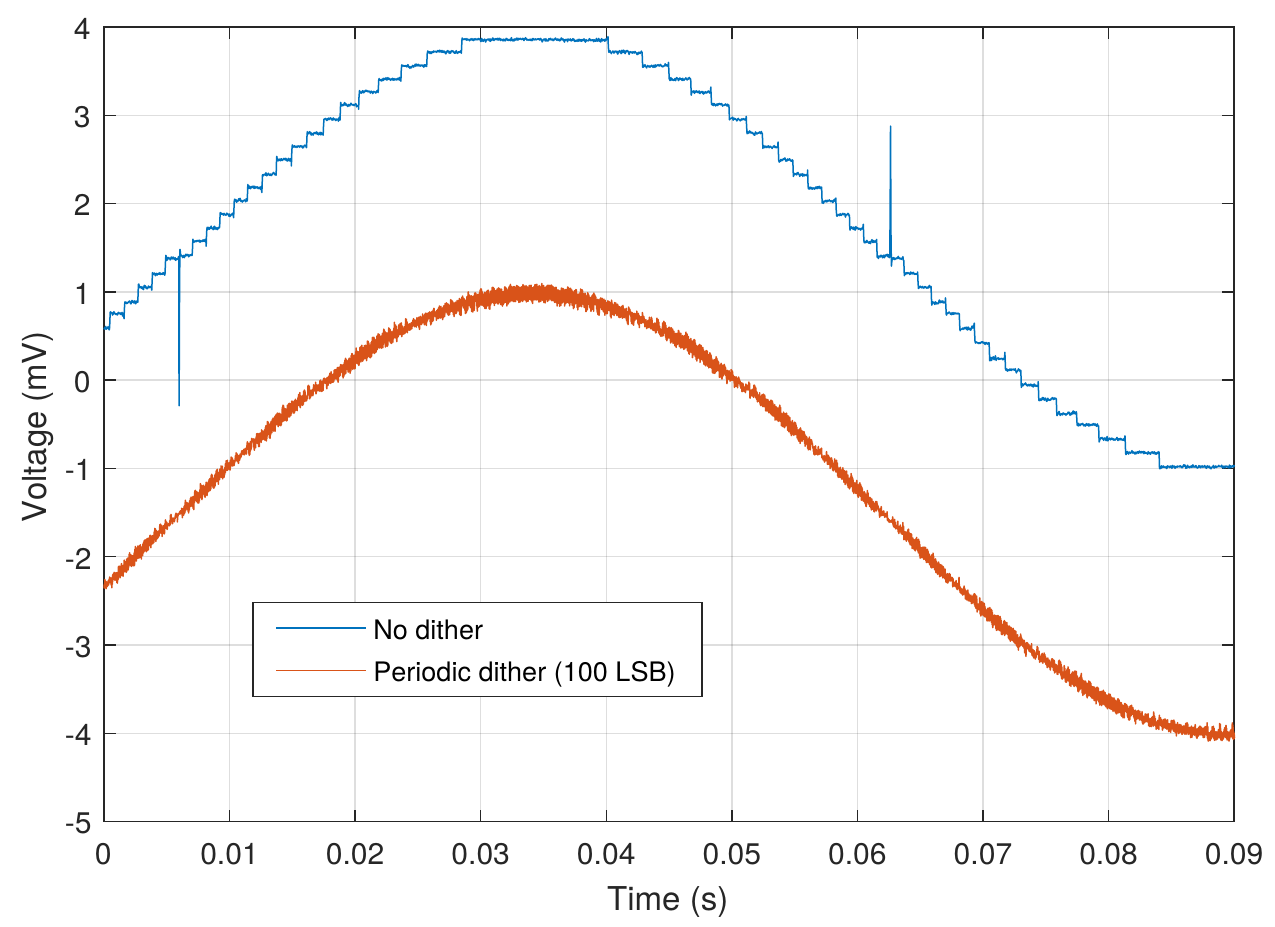
One method that has not been studied in detail yet is large-scale dithering, which can mitigate element mismatch, as well as glitches, and possibly other effects. Work is needed to find ways to maximise the effect of such dither signals, and to study what happens when dither is applied to closed-loop systems.
The exact scope, content and outcomes of the project will be agreed upon with the students considering their background and interests.
Expected outcomes
- Learning how to use rapid prototyping methods (LabVIEW FPGA or MathWorks HDL Coder) to produce high-speed digital-analog converter device interfaces.
- Building prototype printed circuit boards (PCBs) to do testing.
- Learning how to do closed loop control at high speed using FPGAs and using FPGAs for hardware-in-the-loop (HIL) simulations.
- Learning how to measure linearity and performance of converters.
- Using existing and developing new models of non-linear and non-ideal effects in digital-analog converters.
- Determining how well the models fit with actual digital-analog converter behaviour (model validation).
- Understanding how different dither signals impact the distortion in digital-analog converters; determine the model properties.
- Studying how the introduction of feedback control impacts the effect of the dither signals.
- Using optimisation techniques to find optimal dither signals that minimise distortion and error (applicable frameworks can be model predictive control or various input shaping methods).
Resources
- National Instruments FPGA board, or Zedboard with HDL Coder support package.
- LabVIEW and/or MATLAB with sufficient licenses for code generation.
- Digital and analog circuit components and ICs.
- Manufacturing of printed circuit boards.